Mapping Azure Container Instance (ACI) to Custom Domain
I recently had a requirement to map my Docker Container instance to a custom subdomain. One of the way to achieve this is mapping the Container FQDN with CNAME in Domain register portal.
What is FQDN - Fully qualified domain name
what is CNAME : A Canonical Name record
Tomcat container is used in this project to deploy the webapp. The WAR & Dockerfile used in this project is available in Github account Chennaitechie.
I have built the docker image (considering you are aware of how to build docker image) in local desktop now it needs to be pushed into Azure Container Repo.
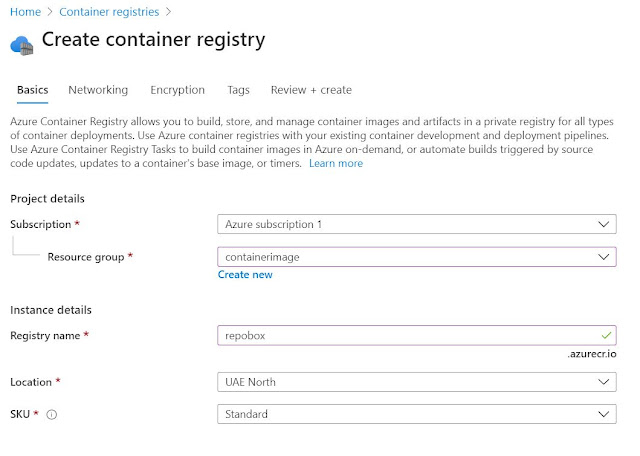
1. Create Azure container registry. Container registry is used as a repo for container images.
In this project i have name by Registry name as
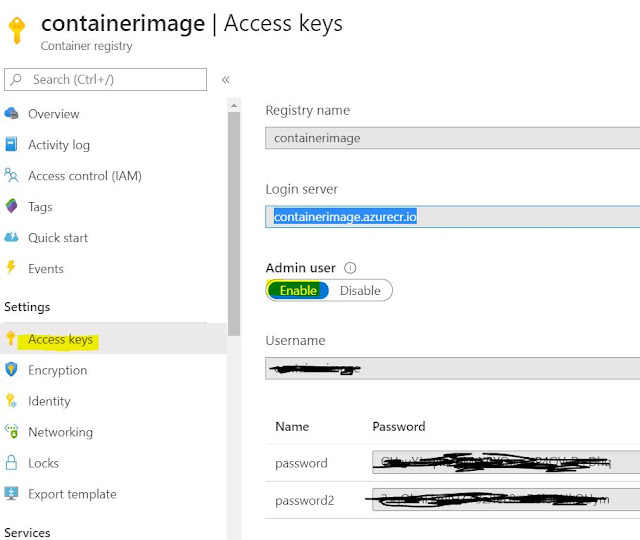
2. Next step is to enable user access for the container registry created . Go to container setting and select access key.
3. Login into Azure Container Registry , Open power shell and type in the command docker login "Container Registry Name" in this project my registry name is containerimage.azurecr.io
execute the cmd and you will have an option to key your username and password from access key page.
4. Docker image should be taged prior to pushing the image into azure container repo.Use docker tag to create an alias of the image with the fully qualified path to your registry. I have used namespace webapp to avoid clutter in root of the registry.
docker tag "local container name" "New tag name"
5. Now lets push the docker image from your local computer to Azure Container Repo and it is a straight forward approach docker push "container name tag"
docker image is transferred to azure and it is ready for action.
6. Select Container instance and add new container to bring up below configuration page.
Image source is selected as Azure Container Registry which will bring up options to select the registry and images available in the repo
7. Select network configuration we need to assign DNS name and open port 8080 which will be used by tomcat .
select Review+Create. Tomcat Container should be up and running copy the dns label name under overview and navigate to port 8080 and the webapp name.
FQDN for this container is tomcat.centralus.azurecontainer.io now contact your domain register to update the CNAME record for your domain or you can do it yourself if you have access to domain management portal.
CNAME record got activated within less than a hour. Thanks for reading !!!
Reference: Azure Container Instance (ACI)